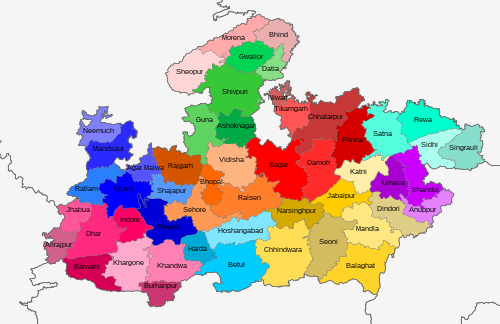
Madhya Pradesh District Map PDF Download
Madhya Pradesh, with an area of 3, 08, 000 sq.km. is the second largest state in India after Rajasthan. It is a part of peninsular plateau of India lying in north central part, whose boundary can be classified in the north by the plains of Ganga-Yamuna, in the west by the Aravali, east by the Chhattisgarh plain and in the south by the Tapti valley and the plateau of Maharashtra. The topography of Madhya Pradesh is defined by the Narmada Sone Valley. It is a narrow and long valley extending through almost the whole of the state from east to west. Sone valley forms the upper part; Shahdol and Sidhi districts lie in this valley. The lower part forms the Narmada valley. It has an average elevation of 300 m above MSL and is covered with alluvial soil. Jabalpur, Mandla, Narsinghpur, Hoshangabad, Raisen, Khandwa, Khargone and Barwani districts lie in this region. The Sone valley is narrower than Narmada valley and alluvial deposit is also comparatively poor and thin, therefore Narmada valley is more important than Sone valley for agricultural activities. To the north of this valley lie the Central Highlands, to the south the Satpura-Maikal ranges and to the south-east, the eastern plateau. These three form the natural physiographic regions-into which the state is divided. The Central Highlands are spread between the Narmada-Sone valley and the Aravali ranges to the west in a triangular form. The highlands slope towards the north and drain into the Yamuna. The central highlands region in the state includes the following four uplands: The Rewa-Panna plateau is one, also known as the Vindhyan plateau, lies in the north- eastern part of the central highlands. The main rivers flowing in the area are Ken, Sonar, Barna and Tons. Rewa, Panna, Satna, Damoh and Sagar districts lie in this region.The other is Bundelkhand plateau located to the north-west of the Rewa-Panna plateau. Datia, Chhatarpur, Panna, Tikamgarh and parts of Guna and Shivpuri districts forming the northern part of the state lie in this region. The plateau is bounded in north-east by Vindhyan escarp lands or Rewa-Panna plateau. The average height of the region is 350-450 m above MSL and general slope is towards north. The main rivers flowing in the area are Betwa, Dhasan and Jamner which finally join Yamuna. Central India plateau is the third that lies to west of Bundelkhand plateau. Shivpuri, Morena and Gwalior districts exist in this region. This plateau has an average elevation of 450 m on highlands and 150-450 m above MSL in valleys. Chambal, Kali Sindh and Parvati are the main rivers flowing in this area. The fourth Malwa plateau covers almost the entire western Madhya Pradesh. The plateau is bounded in the north by Chambal and in south by the Narmada. The average elevation ranges between 300-500 m above MSL. Shajapur, Dewas, Indore, Ujjain, Dhar, Ratlam and parts of Sehore and Jhabua districts lie in this region. Bhopal is situated at the eastern edge of the Malwa plateau. Shipra, Parvati, Kali Sindh, Gambhir and Chambal rivers flow through the Malwa plateau. It also forms the water divide between the Ganga and the Narmada basin. The soil in the area is black cotton as a result of weathering of basalts.
Language
Hindi, the official language of Madhya Pradesh, is the most widely spoken and easily understood even in remote corners of the state. For a large number of people in the major towns and cities and for the business class English is the second language. It is widely spoken by those engaged in the hospitality and service industry. One would see words of English and Hindi both used on signages, milestones, shops and offices signboards. Malwi, Bundeli, Bagheli, Nimari are the commonly spoken regional dialects. There are several dialects which are spoken.
Population
The population of Madhya Pradesh is over 7 crore. More than 75% of the population resides in villages whose main occupation is agriculture, while the rest of the population lives in towns. The majority population is Hindu with Muslims making up the largest minority community. The tribes of Madhya Pradesh constitute over 20 % of the state’s population and are mainly concentrated in southern southwestern and eastern parts of the state. The social customs prevalent among different tribes and castes vary more due to variation in their habitat and surrounding geographical conditions. For earnings they depend upon agriculture, forest produce and local craft. With improved communication and growth in the economy, the tribal’s way of living is changing.
Baigas believe themselves to be descendents of Dravid and this tribe is found in Mandla, Balaghat, Shahdol and Sidhi districts. Saharia inhabit north-west area mainly in the districts of Gwalior, Shivpuri, Bhind, Morena, Sheopur, Vidisha and Raisen. Most Saharias are cultivators. Bharia tribe has major concentration in Jabalpur and Chhindwara districts of Madhya Pradesh. The place Patalkot in Chhindwara has almost 90% population of Bharias. They work as agriculture labourers and work upon bamboo to create beautiful baskets and other items.
Gond is the best known tribe and forms the largest group in Madhya Pradesh. They mainly inhabit areas on both sides of Narmada in Mandla, Chhindwara, Betul and Seoni regions and the hilly terrains of Vindhya and Satpura regions. Agaria, Pradhan, Ojhan, Solahas are the descendant tribal groups originating from Gonds, with two sub-castes – Rajgond and Datoliya.
Bhil, the second largest tribe, is largely concentrated in areas around Jhabua, Khargone, Dhar and Ratlam. They are regarded as warrior with fine inherited guerrilla tactics and archery skills. Korku tribal community is administered by the head of a panchayat called Sarpanch and they are found in Hoshangabad, Betul, Chhindwara, Harda and Khandwa districts of Madhya Pradesh. Santia is a tribe of Malwa, who believe themselves to be originally a martial Rajput tribe. They prefer to remain nomadic. Mainly of labour class, Kols are found in Rewa, Sidhi, Satna, Shahdol and Jabalpur districts. This caste finds mention even in ancient puranas and the famous epics of Ramayana and Mahabharata and they are highly religious minded and staunch believer of Hindu mythology. Lesser known tribes like Dhanuk, Panika, Saur still form an important group.
Climate
Like other parts of India, Madhya Pradesh also has three major seasons – Summer Monsoon and Winter. During summer (March-June), the temperature in the entire state ranges above 29.4°C. In general, the eastern parts of Madhya Pradesh are hotter than the western parts. The regions like Gwalior, Morena and Datia record temperature of over 42°C in the month of May. The humidity is relatively very low and the region usually experiences frequent mild dust storms. The south-west Monsoon usually breaks out in mid June and the entire state receive a major share of its rainfall between June and September. The south and south-east regions tend to experience a higher rainfall whereas the parts of north-west receive less. Mandla, Balaghat, Sidhi, Jabalpur and other extreme eastern parts receive more than 150 cm rainfall. The districts of western Madhya Pradesh receive less than 80 cm rainfall.
The winter season starts from the month of November. The temperature remains low in the northern parts of the state in comparison to the southern parts. The daily maximum temperature in most of the northern part in the month of January remains between 15 and 18°C. The climate is generally dry and pleasant with a clear sky.
Madhya Pradesh District Map
There are 55 districts in Madhya Pradesh. Here is the list of Madhya Pradesh districts.
Shahdol division. Anuppur district. Shahdol district. Umaria district. Dindori district.
Ujjain division. Agar Malwa district(split from Shajapur district on 16 Aug 2013) Dewas district. Mandsaur district. Neemuch district. Ratlam district. Shajapur district. Ujjain district. Nagda district (approved by cabinet on 18 March 2020)
Niwari District is one of the 55 Districts of the Madhya Pradesh. This district was formed on 1 October 2018. Niwari is the smallest district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Largest District is biggest in MP is Chhindwara and Area 11815 km²
- Smallest District is biggest in MP is Niwari and Area 1170 km²
| No. | Name of District | Area (sq km) | Population | Name of Head Quarters |
| 1 | Agar Malwa | 2,785 | 480,000 | Agar |
| 2 | Alirajpur | 3,182 | 728,999 | Alirajpur |
| 3 | Anuppur | 3,746 | 749,237 | Anuppur |
| 4 | Ashoknagar | 4,674 | 845,071 | Ashoknagar |
| 5 | Balaghat | 9,229 | 1,701,698 | Balaghat |
| 6 | Barwan | 5,432 | 1,385,881 | Barwan |
| 7 | Betul | 10,043 | 1,575,362 | Betul |
| 8 | Bhind | 4,459 | 1,703,005 | Bhind |
| 9 | Bhopal | 2,772 | 2,371,061 | Bhopal |
| 10 | Burhanpur | 2,473 | 757,847 | Burhanpur |
| 11 | Chhatarpur | 8,687 | 1,762,375 | Chhatarpur |
| 12 | Chhindwara | 1,1815 | 2,090,922 | Chhindwara |
| 13 | Damoh | 7,306 | 1,264,219 | Damoh |
| 14 | Datia | 2,038 | 786,754 | Datia |
| 15 | Dewas | 7,020 | 1,563,715 | Dewas |
| 16 | Dhar | 8,153 | 2,185,793 | Dhar |
| 17 | Dindori | 7,427 | 704,524 | Dindori |
| 18 | East Nimar | 10,779 | 1,310,061 | Khandwa |
| 19 | Guna | 6,485 | 1,241,519 | Guna |
| 20 | Gwalior | 5,214 | 2,032,036 | Gwalior |
| 21 | Harda | 3,339 | 570,465 | Harda |
| 22 | Hoshangabad | 6,698 | 1,241,350 | Hoshangabad |
| 23 | Indore | 3,898 | 3,276,697 | Indore |
| 24 | Jabalpur | 5,210 | 2,463,289 | Jabalpur |
| 25 | Jhabua | 6,782 | 1,025,048 | Jhabua |
| 26 | Katni | 4,927 | 1,292,042 | Katni |
| 27 | Mandla | 5,805 | 1,054,905 | Mandla |
| 28 | Mandsaur | 5,530 | 1,340,411 | Mandsaur |
| 29 | Morena | 4,991 | 1,965,970 | Morena |
| 30 | Narsinghpur | 5,133 | 1,091,854 | Narsinghpur |
| 31 | Neemuch | 4,267 | 826,067 | Neemuch |
| 32 | Niwari | —– | 23,724 | Tikamgarh |
| 33 | Panna | 7,135 | 1,016,520 | Panna |
| 34 | Raisen | 8,446 | 1,331,597 | Raisen |
| 35 | Rajgarh | 6,154 | 1,545,814 | Rajgarh |
| 36 | Ratlam | 4,861 | 1,455,069 | Ratlam |
| 37 | Rewa | 6,434 | 2,365,106 | Rewa |
| 38 | Sagar | 10,252 | 2,378,458 | Sagar |
| 39 | Satna | 7,502 | 2,228,935 | Satna |
| 40 | Sehore | 6,578 | 1,311,332 | Sehore |
| 41 | Seoni | 8,758 | 1,379,131 | Seoni |
| 42 | Shahdol | 6,205 | 1,066,063 | Shahdol |
| 43 | Shajapur | 6,196 | 1,512,681 | Shajapur |
| 44 | Sheopur | 6,585 | 687,861 | Sheopur |
| 45 | Shivpuri | 10,278 | 1,726,050 | Shivpuri |
| 46 | Sidhi | 10,256 | 1,127,033 | Sidhi |
| 47 | Singrauli | 5,672 | 1,178,273 | Singrauli |
| 48 | Tikamgarh | 5,048 | 1,445,166 | Tikamgarh |
| 49 | Ujjain | 6,091 | 1,986,864 | Ujjain |
| 50 | Umaria | 4,026 | 644,758 | Umaria |
| 51 | Vidisha | 7,371 | 1,458,875 | Vidisha |
| 52 | West Nimar | 8,020 | 1,873,046 | Khargone |
Madhya Pradesh (MP) District Map PDF Download (English Version) — Click Here